Genetic Factors Influencing Plaque Psoriasis

Intro
Plaque psoriasis is more than just a skin ailment; it’s a complex interplay of genetics and environment encapsulated in a stubborn inflammatory response. Understanding this condition goes beyond surface appearances, digging into the genetic codes that lay the foundation for inheriting susceptibility. It’s like peeling an onion, revealing layers of information that explain why some individuals find themselves afflicted while others remain untouched.
Genetics plays a pivotal role in the manifestation of plaque psoriasis. Certain gene variants have been linked to the likelihood of developing the condition. This exploration will illuminate how heritability influences this intricate skin disorder and identify key genetic players in its pathogenesis.
The heritable nature of plaque psoriasis suggests that one’s family history can serve as a telling sign. Nevertheless, genetics alone does not paint the entire picture. Environmental factors, such as stress, diet, and skin injuries, can act as triggers that unleash the tangling genetic predisposition, creating a perfect storm that leads to the outbreak of psoriasis.
As we embark on this comprehensive exploration, we will survey the latest findings in genetic research surrounding plaque psoriasis, assess their significance in the scientific community, and ponder the real-world applications of these findings. Through this inquiry, we hope to shed light on how knowledge of genetics might inspire future therapeutics and improve the lives of those managing plaque psoriasis.
Preface to Plaque Psoriasis
Understanding plaque psoriasis isn't just a matter of knowing a skin condition—it's about grasping the significant genetic and environmental factors that shape its existence. This inflammatory disorder surfaces on the skin as red patches coated with silvery scales, a visible reminder of deeper, underlying biological mechanisms at work. Through this exploration, we'll shed light on essential aspects of the disease that often escape general discussion.
The importance of diving into plaque psoriasis lies in its widespread prevalence and impact on both individuals and healthcare systems. It affects millions globally, eliciting not only physical discomfort but also psychological stress and social stigmatization. An accurate and insightful overview of this condition enables better awareness among patients, caregivers, and healthcare professionals alike.
Overview of Plaque Psoriasis
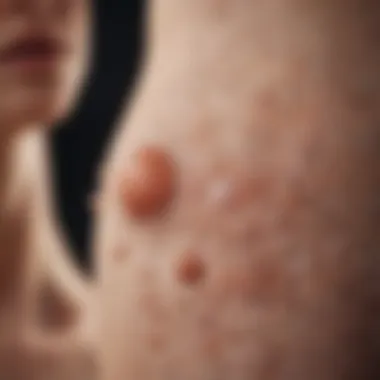
Plaque psoriasis is one of the most common forms of psoriasis, characterized by raised, inflamed lesions on the skin known as plaques. These patches, often found on elbows, knees, and the scalp, arise from an accelerated skin cell turnover driven by dysregulation in the immune response. Essentially, this condition reveals an intriguing interplay between the body's immune system and skin functions, giving rise to symptoms that can sometimes feel overwhelming.
According to recent studies, most individuals with plaque psoriasis experience symptom flare-ups that can be triggered by various factors, such as infections, stress, or even weather changes. While the root cause remains a combination of genetic and environmental influences, the experience of living with plaque psoriasis can be incredibly nuanced and personal.
Prevalence and Impact
The incidence of plaque psoriasis affects approximately 2-3% of the global population, equating to millions of individuals. Statistics show a slight prevalence among Caucasians compared to other ethnic groups, but this does not diminish the condition's seriousness. The impact of plaque psoriasis goes beyond the skin. It inhibits daily functioning for many, straining both personal and professional relationships.
"Psoriasis is not just a skin disease; it’s a whole-body condition that influences the quality of life."
Individuals living with plaque psoriasis often report feelings of self-consciousness, which can lead to anxiety and depression. According to health surveys, patients may face challenges in social situations or workplaces where skin visibility becomes a point of focus. The stigma surrounding visible skin conditions adds an extra layer of complexity, leading to a ripple effect that can reach deep into emotional well-being.
By understanding these elements, both medical research and healthcare practices can be better directed toward offering more holistic care to those affected. More than just a dermatological concern, plaque psoriasis requires an integrated approach—recognizing the genetic underpinnings and paying attention to the environmental triggers. Only then can effective treatments and management strategies truly evolve.
Understanding Genetic Factors
Understanding the genetic factors behind plaque psoriasis is paramount in grasping how this complex disorder operates within individuals. Genetic elements contribute significantly to the biological architecture of psoriasis, paving the way for targeted research and subsequent therapies. With plaque psoriasis being both a chronic and often debilitating condition, unearthing the genetic backgrounds not only clarifies individual risk factors but aids in shaping preventive strategies and treatment plans.
Genetics forms the backbone of many diseases, and psoriasis is no different. The genetic landscape of plaque psoriasis, which implicates various genes and their interactions, offers insights into how the immune system and skin cells behave abnormally. This understanding helps bridge the gap between bench-side molecular biology and bedside clinical applications, allowing us to tailor treatments that specifically address genetic predispositions. Moreover, it injects a sense of urgency and focus into ongoing research aimed at elucidating the causative pathways in psoriasis.
Genetic Basis of Diseases
The genetic basis of diseases like plaque psoriasis has become a focal point in contemporary research. Plaque psoriasis involves an array of skin lesions characterized by red patches covered with silvery scales. At its core, the disease arises from a dysfunctional immune response—a response that is largely dictated by genetic expression.
Several key aspects to consider include:
- Key Genes and Pathways: Genes such as IL-23 and IL-17 are crucial as they regulate the immune responses, leading to the inflammatory processes characteristic of psoriasis.
- Major Histocompatibility Complex (MHC) genes play a significant role in the presentation of antigens and subsequent activation of immune cells. Variations in these genes might predispose individuals to psoriasis.
- Epigenetic Factors: Beyond mere genetics, epigenetic changes can influence how genes are expressed without altering the actual DNA sequence. Such influences can be brought upon by environmental triggers, setting the stage for the manifestation of plaque psoriasis in genetically susceptible individuals.
The interplay between these genetic components composes a complex portrait of how psoriasis develops. To fully appreciate this, researchers often conduct studies exploring genomic sequences to identify specific markers or variations that correlate with the severity and response to treatment of the disease.
Heritability Studies
Heritability studies have made sizable contributions to our understanding of plaque psoriasis. These studies essentially assess how much genetics can account for the likelihood of developing the disorder as opposed to environmental causes. Understanding these contributions can help elucidate the hereditariness of plaque psoriasis, with some estimates suggesting that genetic factors could account for roughly 60-90% of cases.
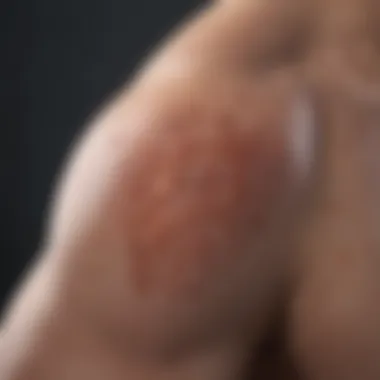

Key findings from heritability studies include:
- Twin studies indicate a higher concordance rate for psoriasis among identical twins compared to fraternal twins, reinforcing the genetic basis.
- Family studies show that individuals with a first-degree relative diagnosed with plaque psoriasis exhibit a higher risk of developing the condition themselves.
- Research exploring gene-environment interactions helps clarify why not all genetically predisposed individuals develop psoriasis, indicating that environmental influences, in tandem with genetic factors, play a critical role in the onset of the disease.
These insights help paint a clearer picture of plaque psoriasis, showing that while genetics is a major player, the environment can tip the scales. Considering this complexity allows for a more comprehensive approach to prevention and treatment, catering specifically to individual needs based on genetic profiling.
"The intricacies of genetics in psoriasis will steer future treatment pathways toward a more personalized approach."
As we delve deeper into these areas of genetic research, we grow closer to understanding the full spectrum of how plaque psoriasis presents and progresses, as well as giving hope for novel therapeutic interventions tailored to individuals' unique genetic makeups.
Key Genes Involved in Plaque Psoriasis
Understanding the genes that play a part in plaque psoriasis is vital. They give us clues about why some folks are more prone to this skin condition than others and how we might treat it effectively. As we dive deeper into this section, we'll uncover specific genes and their roles in Psoriasis. This knowledge not only sheds light on the causes of this ailment but also opens pathways for personalized treatments.
Major Histocompatibility Complex (MHC)
When it comes to genetics and immune response, the Major Histocompatibility Complex (MHC) stands out as a significant player. It contains a bunch of genes that help regulate the immune system. In regards to plaque psoriasis, certain MHC alleles are linked to increased susceptibility.
- MHC Class I and II molecules help recognize foreign pathogens. In psoriasis, an overactive immune response is often triggered by misinterpretation of benign skin components.
- Studies have found that particular MHC alleles—like HLA-Cw6—are strongly associated with an increased risk. Individuals carrying this allele are more likely to develop the disease than those without it.
It's quite clear, the MHC sets the stage for how our body reacts. Getting into this gene's role in plaque psoriasis can help researchers pinpoint new therapeutic strategies. By understanding variations in MHC, we can assess risk factors and tailor personalized treatment plans, making it a focal point in psoriasis research.
IL-23 and IL-17 Pathways
The interplay of the IL-23 and IL-17 pathways has garnered much attention in the realm of psoriasis. Both of these pathways are crucial for maintaining immune homeostasis, but when things get out of whack, they contribute to the inflammatory processes that characterize plaque psoriasis.
- IL-23 is a cytokine that promotes the survival and maintenance of T helper 17 (T7) cells, which produce IL-17.
- IL-17, in turn, leads to the production of other pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines. These substances are responsible for driving the skin's inflammatory response, leading to the characteristic plaques seen in psoriasis.
Recent advances have seen the development of biologics that specifically target the IL-23 and IL-17 pathways. Therapies like ustekinumab target IL-23, while secukinumab focuses on IL-17. This targeting not only provides relief from symptoms but also demonstrates the direct implications of understanding these pathways in developing effective treatments.
Other Susceptibility Genes
Beyond the MHC and the IL-23/IL-17 pathways, other genes also play a critical role in influencing susceptibility to plaque psoriasis. Among them are:
- CARD14: This gene is involved in the immune response. Variants here are linked to a higher risk of developing psoriasis, indicating its potential role in skin barrier disruption and immune dysregulation.
- TNF-α: This gene encodes a cytokine involved in systemic inflammation. Medications that inhibit TNF-α, such as etanercept and adalimumab, have shown effectiveness in managing psoriasis.
- IL-12B: Another important cytokine that influences T cell responses, IL-12B variants have been associated with increased risk for autoimmune disorders, including psoriasis.
In summary, the exploration of susceptibility genes paints a multifaceted picture of plaque psoriasis. By identifying these genetic players, we stand on the brink of precise medical strategies that can potentially change the landscape of treatment in this chronic condition. Understanding these genes gives researchers the tools to tackle psoriasis from a genetic angle, leading to breakthroughs in therapies that could revolutionize care.
Gene-Environment Interactions
Understanding how genes and environmental factors come together to influence plaque psoriasis is crucial in grasping the full picture of this complex condition. This section delves into the essence of gene-environment interactions, illuminating their significance in the manifestation and management of psoriasis. The interaction between one's genetic predisposition and various external factors does not just provide an explanation for disease development; it also guides the approach to treatment and prevention.
Role of Environmental Triggers
Environmental triggers are pivotal in activating psoriasis in genetically predisposed individuals. These triggers can vary significantly, ranging from infections to weather conditions, and stress to diet. Some common environmental elements that have been studied include:
- Infections: Certain viral and bacterial infections, particularly streptococcal throat infections, have shown a clear link to the onset of psoriasis flares. The immune response to these infections can inadvertently provoke skin cell turnover, leading to plaque formation.
- Weather: Seasonal changes often bring about fluctuations in psoriasis symptoms. For instance, many patients find that cold, harsh winter weather exacerbates their condition, while sunlight exposure in summer tends to alleviate symptoms. This is partly because UV light helps slow down the rapid growth of skin cells.
- Medications: Certain medications, like lithium or beta-blockers, may act as catalysts for psoriasis flare-ups, showing that treatment for other conditions can sometimes complicate psoriasis management.
This interplay signifies how understanding environmental triggers can shape intervention strategies for individuals. It emphasizes the need for a tailored approach to care that considers both genetic and environmental aspects.
Psychological Stress and Psoriasis
The psychological landscape is a significant player in the development and exacerbation of plaque psoriasis. Stress seems to be a double-edged sword; not only can it trigger new episodes, but it can also lead to worsening of existing conditions. The link between psychological stress and psoriasis exists on both physical and cognitive levels. Stress can lead to inflammation, which is already a core component of psoriasis pathology. Furthermore, patients often feel a negative cycle of stress impacting their self-esteem due to visible symptoms.


"An alarming number of individuals with psoriasis report feeling isolated and stigmatized, which can exacerbate psychological distress."
The following are significant aspects to consider:
- Emotional Repercussions: Feelings of helplessness or depression are common among psoriasis sufferers, making it essential to incorporate psychological interventions alongside dermatological treatment.
- Coping Mechanisms: Mindfulness techniques, therapy, and stress-reduction practices can positively impact psoriasis management by helping patients develop better coping mechanisms.
By comprehensively addressing both the physical and psychological elements of stress, a more suitable and effective treatment framework can emerge.
Lifestyle Factors and their Impact
Lifestyle choices carry weighty consequences in the management of plaque psoriasis. The way one lives—what they eat, how often they exercise, and even their sleep patterns—can play a role in disease severity and flare-ups. Here are some key lifestyle factors that deserve attention:
- Diet: A diet high in anti-inflammatory foods, such as fruits, vegetables, and omega-3 fatty acids, can help mitigate symptoms. Conversely, processed foods, sugars, and excessive alcohol can trigger inflammation, potentially leading to flare-ups.
- Physical Activity: Regular exercise enhances blood flow, eases stress, and can help control weight, all of which are crucial for maintaining skin health.
- Sleep: Quality sleep is often overlooked in its importance. Inadequate sleep may lead to higher levels of stress hormones, complicating the psoriasis condition.
In summary, being mindful of these lifestyle factors can empower individuals with plaque psoriasis to take charge of their health, ultimately leading to better management of their condition.
Latest Advances in Genetic Research
The field of genetic research is constantly evolving, particularly in the realm of complex diseases like plaque psoriasis. Recent advancements have opened new avenues for understanding its underlying mechanisms, which lie not just in isolated genetic factors but also in the intricate interplay of these factors within biological pathways. This section aims to highlight these advances and their significance, focusing on how they pave the way for innovative treatment approaches and enhance our understanding of the disease etiology.
Genome-Wide Association Studies (GWAS)
Genome-Wide Association Studies (GWAS) have revolutionized our grasp of genetic variations associated with complex diseases. This method enables researchers to scan genomes from many participants to find genetic markers linked to plaque psoriasis. By analyzing vast amounts of data, GWAS have identified several single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) that correlate with increased risk of developing this condition.
Research has uncovered numerous genetic loci, such as those found in the IL-23 receptor pathway, which are pivotal in psoriasis pathogenesis. This kind of information is not just academically thrilling; it holds real promise for shaping personalized medicine strategies, tailoring treatments to an individual's genetic makeup could lead to better outcomes.
"Understanding the genetic blueprint behind plaque psoriasis allows for a shift in the treatment paradigm, transitioning from a one-size-fits-all approach to personalized therapies that account for individual genetic profiles."
Functional Genomics Approaches
Functional genomics explores how genes function in relation to the development of plaque psoriasis. It encompasses a range of techniques, including RNA sequencing and gene expression profiling. These methods help researchers decipher the actual roles that specific genes play in the disease's pathology.
For instance, through functional genomics, scientists have been able to examine how genes implicated in immune response are overexpressed in patients with plaque psoriasis. By going beyond static genetic markers, this approach provides insights into dynamic processes that contribute to disease progression.
This knowledge enables the identification of potential biomarkers for diagnosis and prognosis. In turn, understanding these biological pathways equips researchers with critical information to identify targets for new drugs, which can revolutionize treatment options available for psoriasis management.
CRISPR and Gene Editing Technologies
One of the most exciting frontiers in genetic research is CRISPR technology. CRISPR, a groundbreaking gene-editing tool, allows researchers to modify specific genes with unprecedented precision. Its implications for plaque psoriasis research are profound, especially in terms of understanding disease mechanisms and the potential to develop targeted therapies.
Through CRISPR, scientists can knock out or edit genes that have been implicated in psoriasis. This ability not only facilitates the exploration of gene functions but also opens the door to potential curative therapies. However, the transition from laboratory research to clinical application will require rigorous testing to ensure safety and efficacy in human subjects.
In summary, the advancements in GWAS, functional genomics, and CRISPR present an optimistic landscape for future research in plaque psoriasis. As researchers dive deeper into these approaches, we can anticipate a better understanding of individual pathogenesis, leading us closer to tailored treatment options for patients.
Implications for Treatment and Management
When one thinks about the implications of genetic research for the treatment and management of plaque psoriasis, it becomes clear that we are standing at the brink of a therapeutic revolution. Understanding how genetics plays a role in psoriasis opens up a whole trove of opportunities for tailoring treatment strategies. This section dives deep into those implications, focusing on the potential benefits and considerations that arise from genetic profiling in medical practice.
One of the main advantages of recognizing genetic underpinnings is the potential for tailored therapies. By assessing the genetic variations in patients, healthcare providers can move away from the traditional one-size-fits-all approach. Tailored therapies can optimize outcomes by determining which treatments may be most effective based on an individual’s genetic makeup. For example, certain genetic profiles may suggest a higher likelihood of responsiveness to specific biologics.
Furthermore, incorporating genetic information can reduce trial and error in medication selection. Patients are thus less likely to experience adverse reactions from ineffective treatments. This leads to enhanced patient satisfaction and a better quality of life.


Moreover, in the realm of psoriasis management, there’s an emphasis on precision medicine. This approach focuses on the genetic factors, environmental triggers, and even lifestyle choices unique to each individual, allowing clinicians to design targeted interventions. Think of it as a well-fitted suit versus an off-the-rack variant—customized care just fits better.
"Genetic profiles are not just numbers. They carry the stories of how our bodies react, adapt, and sometimes rebel. Understanding this can lead us to better treatment decisions."
Tailored Therapies Based on Genetic Profiles
Tailored therapies using genetic profiles represent a significant leap forward in managing plaque psoriasis. Specifically, they allow for personalized treatment plans that take into account the unique genetic makeup of each patient. Research indicates that variations in genes related to immune response, particularly in cytokine signaling pathways, can considerably influence the efficacy of different treatments.
- Genetic Testing: Genetic tests can identify which patients are likely to respond effectively to treatments such as biologics. For instance, knowledge of specific SNPs linked to IL-23 and IL-17 pathways can guide clinicians in selecting the right therapeutic agents that may produce better results.
- Pharmacogenomics: This field intersects genetics and pharmacology and can help predict how an individual will respond to drugs. By understanding the patient's genetic response profile, therapeutic dosages can be tailored accordingly, resulting in optimized drug administration at minimal side effects.
- Long-term Management: Tailoring therapies doesn't just stop at the initial treatment plan. Regular genetic assessments can guide ongoing management settings. This allows for timely adjustments in treatment strategies based on how well the patient is responding, thus ensuring better long-term outcomes.
Biologics Targeting Specific Pathways
Another pivotal implication of genetic research in plaque psoriasis is the utilization of biologics that target specific pathways involved in the disease's pathogenesis. The genetic insights we have gleaned from extensive research have led to the development of targeted therapies that address the underlying mechanisms of the disease rather than just its symptoms.
- IL-23 Inhibitors: Genetic studies have shown that IL-23 plays a major role in driving the inflammatory processes in psoriasis. Biologics like guselkumab and tildrakizumab specifically inhibit IL-23, reducing the activation of immune cells that exacerbate skin lesions. For patients with specific genetic markers indicating high IL-23 activity, these treatments may lead to significant improvements.
- IL-17 Inhibitors: Similarly, therapies that target IL-17, such as secukinumab and brodalumab, have emerged as effective options for patients. Genetic variations that correlate with higher levels of IL-17 expression can inform the choice of these biologics, allowing for a tailored approach that maximizes efficacy.
- Other Pathway Modulators: Beyond IL-23 and IL-17, continued research is likely to unveil other promising pathways for intervention. As the genetic landscape of psoriasis unfolds, we can expect to see innovative treatments that better align with the individual genetic profiles of patients.
In summary, acknowledging the genetic basis of plaque psoriasis presents immense implications for treatment. Tailored therapies based on genetic profiles and biologics targeting specific pathways exemplify how medical practices can evolve by integrating genetic insights, ultimately leading to more effective management strategies for those afflicted by this complex condition.
Future Directions in Plaque Psoriasis Research
Understanding the genetic underpinnings of plaque psoriasis is crucial for several reasons, especially as the field moves forward into new territories of discovery and innovation. The insights gained through genetic research pave the way for improved treatments and more personalized management approaches. As researchers comb through the complexities of genes associated with psoriasis, several promising avenues emerge, highlighting the interdisciplinary nature of this investigation.
Promising Areas for Investigation
Numerous promising research areas are ripe for exploration, each with the potential to yield significant breakthroughs in how we understand and treat plaque psoriasis. One key area involves the interaction between genetics and the immune system. The interplay between genetic predispositions and immune responses to environmental factors can illuminate why some individuals develop the disorder while others remain unaffected.
Furthermore, there’s growing interest in microbiome research. The skin microbiome's influence on psoriasis presents an intriguing frontier. Investigating how specific bacteria interact with host genetics may reveal how they can exacerbate or alleviate symptoms. Understanding this connection could lead to new therapeutic strategies that harness beneficial microbial properties.
Additionally, advancements in bioinformatics and machine learning present exciting opportunities for analyzing the large datasets commonly generated in genetic studies. These technologies can reveal previously unnoticed patterns or associations, enhancing our understanding of the disease's complexity.
Lastly, research into epigenetics - changes in gene expression that do not involve alterations to the DNA sequence - could offer ephemeral insights into psoriasis susceptibility. Analyzing how environmental stressors influence gene expression is vital for understanding the pathogenesis of psoriasis and may point to novel therapeutic targets.
Collaborative Research Initiatives
Collaboration is key in the realm of psoriasis research, where the convergence of different disciplines can drive innovation. International consortia, such as the Psoriasis Genetics Consortium, are working together to combine datasets across populations. The scale of these efforts allows for a deeper understanding of genetic variations and their impact on disease expression worldwide.
Another noteworthy initiative is the collaboration between academic researchers and the pharmaceutical industry. These partnerships can help translate basic research findings into viable clinical applications. By pooling resources, expertise, and technology, such collaborations facilitate the rapid development and testing of new treatments tailored to individuals based on their genetic makeup.
Finally, engaging patient advocacy groups and community members in research can enhance the relevance and impact of studies. These grassroots organizations often provide insights into patient experiences that can help shape research questions and therapeutic approaches, making the outcomes more meaningful for those who live with psoriasis every day.
Closure
In summarizing the intricate tapestry of genetic factors underlying plaque psoriasis, it becomes abundantly clear that understanding these elements is crucial for both research advancements and therapeutic interventions. By deciphering the genetic variations and their interactions with environmental triggers, researchers can pave the way for more targeted treatment strategies that minimize suffering and enhance the quality of life for those affected by this skin disorder.
Summary of Key Findings
The exploration of the genetic basis of plaque psoriasis revealed several pivotal insights. The major findings include:
- Heritability: Genetic predisposition plays a significant role, yet environmental factors cannot be overlooked.
- Key Genes: Specific genes like those in the IL-23 and IL-17 pathways are integral to the disease's pathogenesis.
- Gene-Environment Interaction: The relationship between genetic susceptibility and environmental triggers, such as stress and lifestyle choices, is complex and multifaceted.
These aspects converge to underline the necessity for personalized treatment approaches, taking into consideration individual genetic makeups alongside external influences.
The Future of Psoriasis Management
The path forward is laden with promise. The landscape of psoriasis management is evolving, thanks primarily to advances in genetic research and biotechnological innovations. Potential future directions include:
- Gene-Targeted Therapies: Personalized medicine could revolutionize treatment protocols, allowing for therapies designed specifically around a patient's genetic profile.
- Biologics: Continued development of biologic medications targeting specific pathways offers new hope for effective management.
- Research Collaborations: Increased collaboration among researchers and institutions can accelerate discoveries, leading to more robust treatment options.
As we stand on the threshold of new discoveries, it is essential to keep an open dialogue about the implications of these findings. The future of psoriasis management could be vastly different, ushering in novel strategies for those grappling with plaque psoriasis.







